Corn with charcoal rot will have the following symptoms. On grain sorghum stalk rot is caused by F.
Charcoal Rot In Corn Pioneer Seeds
Charcoal rot first becomes noticeable when corn is in the tassel stage or later.
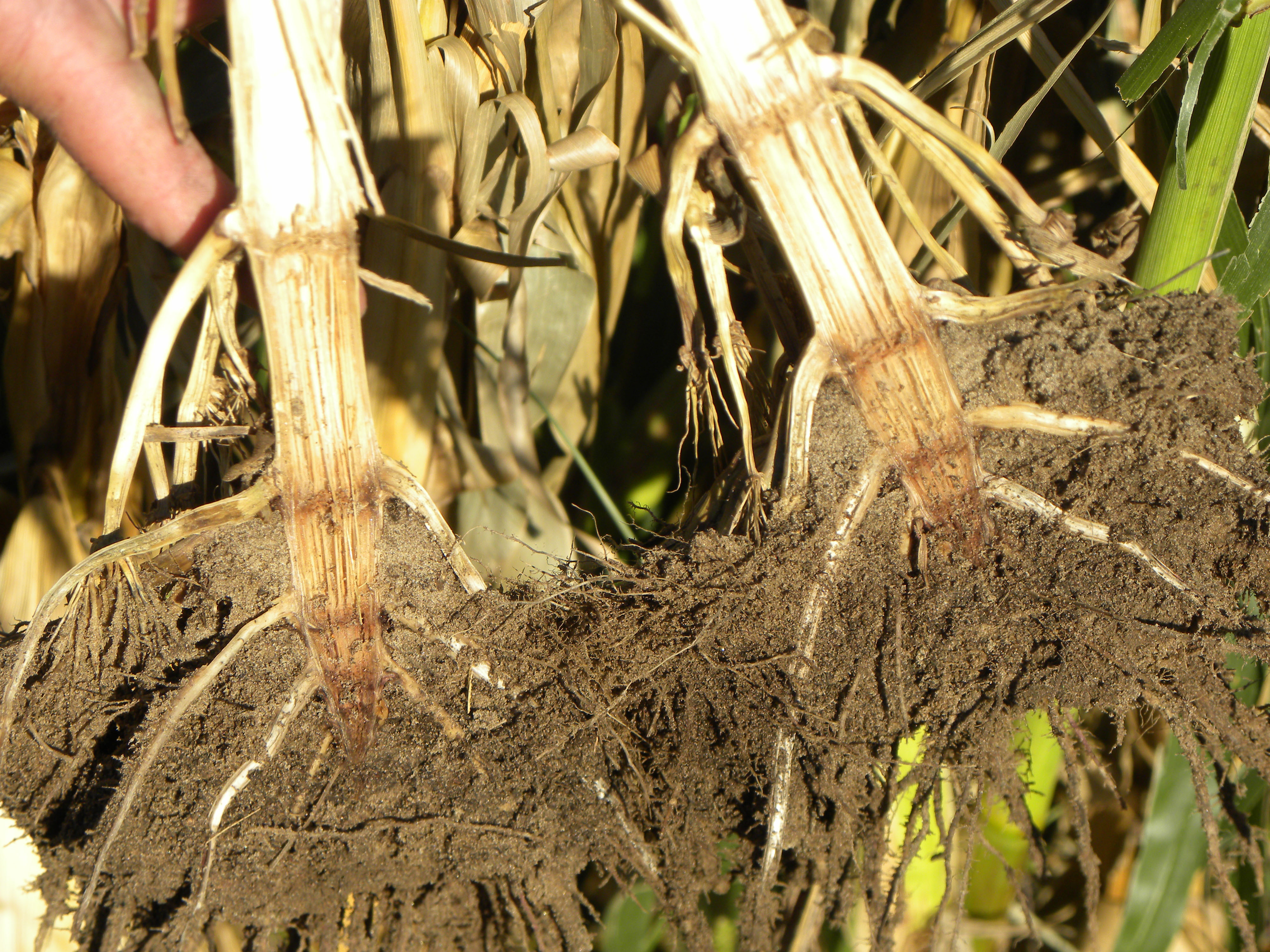

Charcoal stalk rot in corn. Infected stalks become shredded. Charcoal rot is caused by the fungus Macrophomi naphaseolina and effects most grain crops grown in the high plains including corn and soybeans. This will aid in.
There are many host plants that are rotated with corn that the fungus can live in including soybeans. The fungus causes the pith and rind of the stalk to turn a silvery grey caused by development of numerous black microsclerotia. Gibberella stalk rot often causes a.
Dried out or wilting foliage. Plants affected by Diplodia stalk rot have shredded pith and die prematurely. Macrophomina phaseolina the cause of charcoal rot and Colletotrichum graminicola the cause of anthracnose stalk rot.
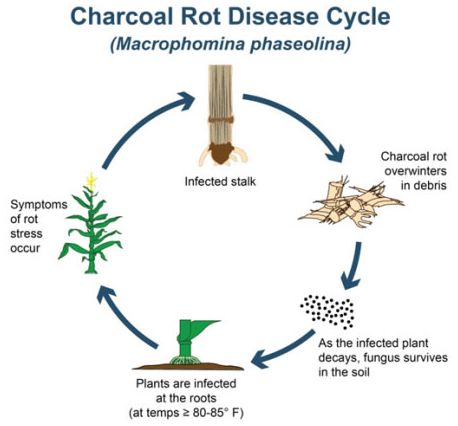
Both diseases are known to survive in crop residue and can survive in the soil for many years. The disease can frequently be minimized by maintaining soil moisture during dry periods after tasseling where irrigation is available. The pith and rind of affected plants appear gray because of the numerous tiny black microsclerotia that develop.
The two most common types of stalk rot in grain sorghum and corn are charcoal rot and Fusarium stalk rot. Gibberella is a very common stalk rot in Indiana and is. The disease which is sometimes also referred to as dry-weather wilt is usually seen when environmental conditions are exactly that extremely hot and dry.
Sweet Corn Charcoal Rot Control. The very tiny black fungal bodies known as sclerotia on the vascular strands of the interior of the stalks contained on the shredded pith give them a charred appearance. Many corn fields were affected by gray leaf spot because of high temperatures and humidity.
Gibberella stalk rot is distributed worldwide and is one of the most common stalk rots in the Corn Belt. However temperatures other than. Charcoal rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina Tassi sclerotial survival was deleteriously affected by a water potential of Goid is a prevalent stalk rot of corn Zea mays L and sorghum approximately -001 bars.
The pith tissue is disintegrated leaving the vascular tissue with a granular gray appearance. Corn is infected during dry periods where the temperature hits 80-85 ºF 27-29 ºC. Premature ripening of fruit.
Charcoal Rot forms from the fungus Macrophomina phaseolina. Typically charcoal rot in corn can been be diagnosed by noting that the pith and stalk rind tissue appear to have a silvery gray appearance due to the development of black microsclerotia which in turn leads to the pith tissue being disintegrated. Corn - Charcoal rot in corn produces symptoms similar to other fungal stalk rots.
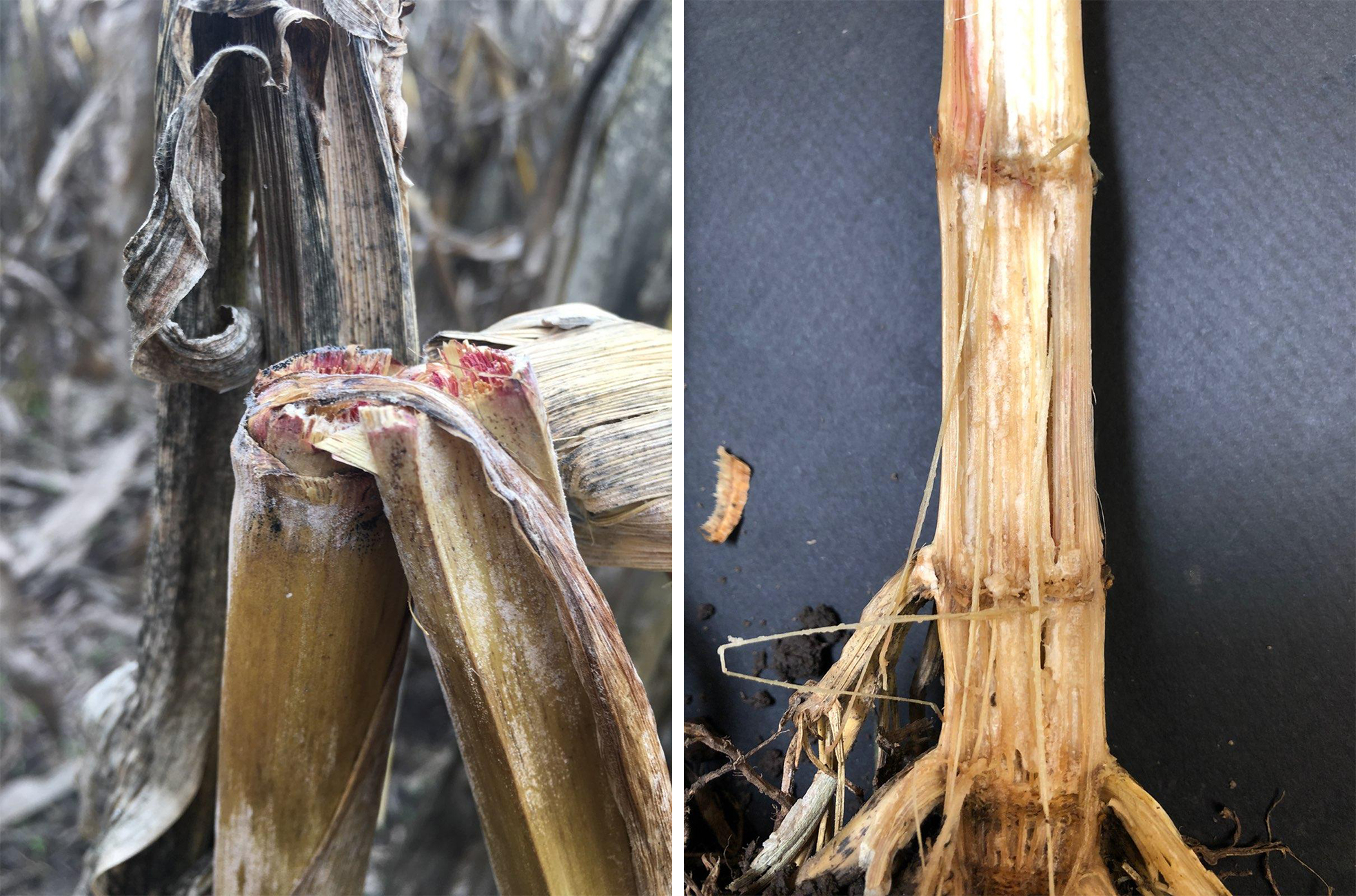
The characteristic sign of charcoal rot is the production of black microsclerotia in the vascular tissue and inside the rind of the stalk. Rotted away pith beneath shredded stalk tissue. Stalk rots have somewhat similar symptoms so it is useful to be able to tell them apart.
Management of charcoal stalk rot is primarily by reduction of stress on the corn crop. Occasionally Diplodia maydis the cause of Diplodia stalk rot can be found on corn but it is much more important as an ear rotting organism. Charcoal rot is one of the few diseases that is more common during drought conditions and so is more likely to affect corn in non-irrigated fields or pivot corners.
Anthracnose stalk rot of corn Photo credit. Bacterial stalk rot appears as brown water soaked lesions accompanied by slimy roots. Vertical splitting of stalk.
The pith is completely rotted leaving stringy vascular strands more or less intact. Charcoal stalk rot dries the pith of the stalks and produces sclerocia that compares to charcoal dust. Small black spherical sclerotia of the fungus are found on and in the vascular strands.
12 rows The time has come to start scouting corn for ear and stalk rots. Charcoal rot Macrophomina phaseolina. Charcoal rot is caused by the fungus Macrophomina phaseolina.
Shredded appearance of stems and stalks. Stresses include high plant populations soil compaction poor fertility drought insect injury and other diseases. The disease is characterized by the presence of many minute black round structures inside the stalk.
For this reason disease tends to be more severe in wheat-corn rotations. Charcoal stalk is usually the cause of premature death of corn plants. Charcoal rot of corn.
They are numerous enough to give the internal stalk tissue a gray color. Charcoal rot begins as a root infection which spreads into the lower stalk internodes and causes early ripening shredding and breaking at the crown of the corn stalk. Leaf diseases predispose plants to stalk rots so if a field had leaf diseases it probably will have stalk rots unless leaf diseases were aggressively controlled with fungicides.
Fusarium graminearum also called Gibberella zeae. Diplodia stalk rot is caused by the fungus Stenocarpella maydis. Diplodia stalk rot of corn.
The causal agent is Gib-berella zeae whose asexual stage is Fusarium graminearum a common seedling pathogen of corn and the causal agent of Fusarium head blight or scab of wheat barley oat and rye. Numerous black dots about the size of a pinhead or smaller can be observed in the lower internodes of the stalk. The stalk will appear gray to black in color.
Charcoal rot begins as a root infection which spreads into the lower stalk internodes and causes early ripening shredding and breaking at the crown of the corn stalk. Gibberella stalk rot is caused by the same fungus that is responsible for Gibberella ear rot on corn and Fusarium head blight of wheat and barley. Stalk rots are possible threat to corn.
Non Technical Summary Many diseases like charcoal stalk rot of sorghum and corn and problems like aflatoxin in corn are a greater risk under drought stress and when there are added biological stress factors like insects and other diseases. Black spots on stems and stalks which give the plant an ashy or charred appearance.

Nebraska Corn Identifying Stalk Rot Diseases 6 Risk Factors Agfax
Stalking The Corn Stalk Rots In Illinois

Scout For Ear And Stalk Rots In Corn Maryland Agronomy News
Charcoal Rot In Corn Pioneer Seeds

Stalk Rot Diseases In Nebraska Corn Fields Cropwatch University Of Nebraska Lincoln

Stalk Rot Symptoms Can Be Misleading In Corn Fields Crop Agupdate Com