Soil testing for nitrate in the surface foot of soil when plants are 6 to 12 inches tall is gaining. Iowa State University developed the corn stalk sampling protocol and interpretation.

Iowa Corn Sampling For The End Of Season Stalk Nitrate Test Agfax
A newly revised publication Use of the End-of-Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test in Iowa Corn Production CROP 3154 is available through the ISU Extension Store.

Stalk nitrate test iowa state. This is assessed by measuring the amount of nitrate - nitrogen present in the lower portion of the corn stalk around the time the plant reaches physiological maturity. If corn had excess nitrogen the corn stalk nitrate level will be high. This test is especially good to diagnose excess nitrogen N availability or application such as with excessive manure or fertilizer N application or when conditions limit yield.
Extensive studies done by Purdue Iowa State and Penn State universities have shown the usefulness of this test in distinguishing between sufficient and excess N situations. The overall suggestion is to wait until crop maturity and sample within 1-3 weeks after kernel black layer. Use of the End-of-Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test in Iowa Corn Production.
Hansen Iowa State University Antonio P. The stalk nitrate test indicated an optimal range from 250-1800 ppm. The use of the pre-sidedress soil nitrate test Brouder Mengel 2003 may also be warranted for fields that regularly test in the excessive category for stalk nitrates in the fall.
John Sawyer Antonio Mallarino A comprehensive update of PM 1584 Cornstalk Testing to Evaluate Nitrogen Management. Both sets of studies showed that a stalk nitrate N concentration above 2000 ppm is indicative of excessive nitrogen having been available to the corn crop. Corn Stalk Nitrate Testing The Corn Stalk Nitrate Test CSNT was developed by Iowa State University agronomists to determine if growers were using the proper amounts of nitrogen for corn production.
This test is especially good to diagnose excess nitrogen N availability or application such as with excessive manure or fertilizer N application or when conditions limit yield. The CSNT provides an assessment of whether the crop had. Their interpretation guidelines are given in Table 1.
Researchers at Iowa Sate University have come up with the stalk nitrate N test as a diagnostic tool in improving N management in corn wwwncagrgovagronomipdffilescornstalkpdf. Sampling for the End-of-Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test. Cornstalk Testing to Evaluate Nitrogen Management PM-1584.
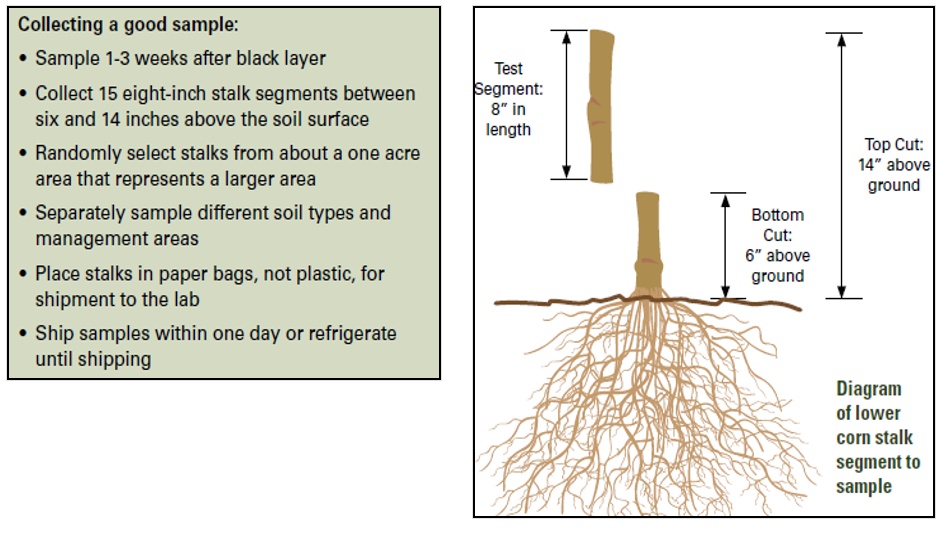
Stalk Nitrate-N Concentration on Nonfertilized Plots o 250 ppm deficient. The stalk nitrate test is based on the concentration of nitrate-N in the lower corn stalk 8 inch segment from 6 to 14 inches above the ground when the plant reaches maturity See Cornstalk testing to evaluate nitrogen management PM 1584. The corn stalk nitrate test CSNT is conducted late in the season and can be a reliable end-of-season indicator of crop nitrogen N status.
Sampling corn stalks this fall will likely be later than normal due to the delayed planting in many Iowa cornfields. The corn stalk nitrate test is a late-season or end-of-season plant analysis on mature corn stalks. Using that criteria and results of additional recent research in Iowa and other Midwestern states an approximate.
You can read details about this test in Iowa State University ISU extension publication CROP 3154 Use of the End-of-Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test in Iowa Corn Production. The publication is written by John Sawyer and Antonio Mallarino professors and extension specialists in agronomy at Iowa State University. This does not work well for silage corn so the suggestion is to collect stalk samples at the time of silage harvest or within 24 hours after harvest as long as no rain between harvest and sampling.
2021 CORNSTALK NITRATE TESTING. If corn did not have sufficient nitrogen the corn stalk nitrate level will be low. It is end-of-season evaluation tool.
Cornstalk testing to evaluate nitrogen management. In general a larger amount of plant-available N in the soil during the time period before plant maturity. Iowa State University D.
Dongs group has invented new soil. The stalk nitrate test is based on the concentration of nitrate-N in the lower corn stalk 8 inch segment from 6 to 14 inches above the ground when the plant reaches maturity ISU Extension publication PM 1584 Cornstalk testing to evaluate nitrogen management. Soil yield potential Stalk nitrate test category Low Optimal Excessive of sites correctly categorized Medium 60 92 71 High 75 56 63 References and other reading Blackmer AM.
Navreets research is the result of a collaboration with Dr. For the 12th consecutive year Bremer Iowa State University Extension and Outreach is offering to collect and test your corn stalks for residual nitrate levels. The publication describing the End-of-Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test was updated in 2018 Use of the End-of-Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test in Iowa.
Concentrations less than 250 ppm are considered a. Extensive studies done by Purdue Iowa State and Penn State universities have shown the usefulness of this test in distinguishing between sufficient and excess N situations. This new publication details how to use the end-of-season plant test to provide information on nitrogen supply to corn for the season that just ended.
To evaluate how well nitrogen fertilizer was utilized by the corn plant. This test gives you information on how well you have managed your nitrogen and doesnt provide information on how much fertilizer N to apply for the coming season. Test category is suggested from 250-2000 ppm nitrate-N in the lower corn stalk.
Iowa State University Extension Bulletin PM 1584. The End-of-Season Cornstalk Test developed at Iowa State University Blackmer Mallarino 1996 allows growers to conduct a post-mortem evaluation of the adequacy of their nitrogen program for the current growing season. This saves you time input costs plus over a series of years help you analyze your fertilizer inputs.
Liang Dongs group from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Iowa State University. The test is described as post-mortem because stalk samples are taken after the grain is physiologically mature. A stalk sap nitrate test on the other hand can provide information about the nitrogen status of corn early enough to make appropriate fertilizer decisions.
Both sets of studies showed that a stalk nitrate N concentration above 2000 ppm is indicative of excessive nitrogen. You can read details about this test in Iowa State University ISU extension publication CROP 3154 Use of the End-of-Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test in Iowa Corn Production. End of Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test Studies conducted at Iowa State University show that nitrogen N status of a corn crop can be assessed by measuring the nitrate concentrations in the lower portions of the cornstalks at the end of the growing season.
The test reflects N availability during the growing season and provides a tool to help growers determine if their N management practices were adequate. Their interpretation guidelines are given in Table 1.
Corn Stalk Nitrate Test Agvise Laboratories

Use Of The End Of Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test In Iowa Corn Production

Use Of The End Of Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test In Iowa Corn Production

Give Careful Consideration To Likely High Soil And Cornstalk Nitrate Levels This Fall Integrated Crop Management

Use Of The End Of Season Corn Stalk Nitrate Test In Iowa Corn Production

Cornstalk Nitrate Interpretation Integrated Crop Management